While the cryptocurrency hype is slowly dying down, a new trend is emerging in the form of dedicated, enterprise-oriented blockchains. Blockchains have many useful qualities that distinguish them from conventional approaches to software development. They’ve already found their place in finance, Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, supply chain management, and other sectors. We believe that healthcare is next in line for blockchain adoption.
In this article, we consider what can be improved in medical software and talk about the role of the blockchain in healthcare improvements. To show how it’s possible to combine the blockchain and healthcare, we explore how to implement a basic medical record management system based on the Hyperledger Fabric network.
Opportunities for improvement in healthcare
Every challenge is an opportunity to make something a bit better. And when it comes to modern medical applications, there’s a lot of room for improvement. Security violations, medical errors, overly complicated insurance claims, an inability to track the status of patients across organizations, and a lack of information exchange between doctors are widespread issues that severely affect medical companies and patient outcomes.
Two of the most salient issues that need to be addressed are data fragmentation and security violations. Let’s look closely at each of them.
Data fragmentation
The problem of extreme data fragmentation exists across the whole healthcare sector. Throughout their lives, people create an enormous quantity of medical records that are stored and processed by various systems. And these systems are usually owned by different, often competing organizations. So collecting a single, coherent medical history from all these distributed records is a true challenge.
Furthermore, data fragmentation leads to other problems such as:
- Diagnostic issues — Without a complete medical history, determining the right diagnosis and optimal treatment becomes quite difficult.
- Insurance-related issues — There’s always a chance that insurance claims won’t be pre-authorized because a patient was unable to provide insurance information or provided false information. To make things worse, insurance claims can even be rejected because of insufficient or missing data.
- Privacy issues — Patient data can be leaked as patients have no control over who has access to their data and when.
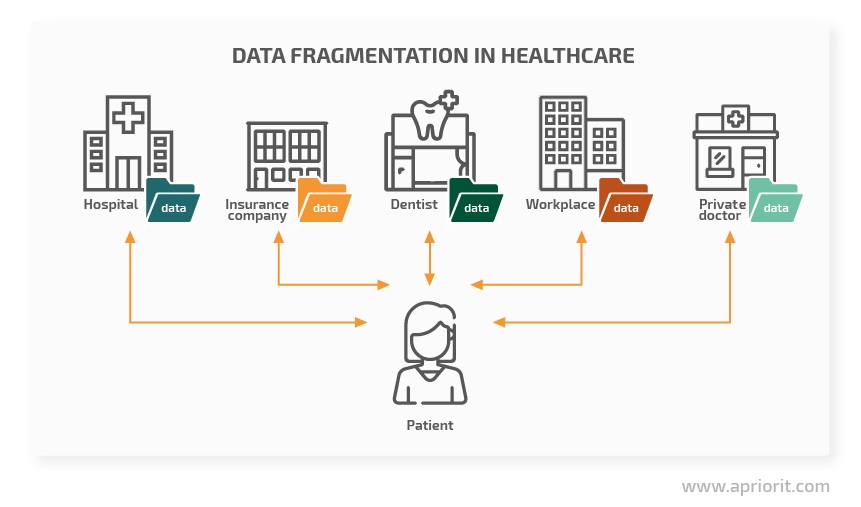
The best way to solve this problem is to come up with a secure and efficient way to consolidate all that fragmented data. However, data consolidation is still on the horizon. In the meantime, there are other urgent matters in healthcare applications that require our attention.
Security violations
Healthcare is one of the most strictly regulated industries, and for good reason. Since every medical application processes tremendous amounts of sensitive personal information, data security needs to be a priority.
One of the most noticeable and expensive problems is fines for non-compliance and regulatory violations. In 2019, the average fine for a HIPAA violation reached over $1.2 million.
These are the most common security violations in the healthcare sector:
- No proper organization-wide risk analysis implementation
- Poor management of security risks
- Insufficient health information access controls
- Disclosures of protected health information (PHI)
- Lack of data encryption or other measures for safeguarding health information
- Denying patients access to their health records
Ignoring these issues when developing a healthcare-specific solution may result in devastating data leaks, regulatory violations, severe reputational damage, and, of course, huge fines. But security isn’t the only problem to keep in mind when working on medical applications.
General improvements in healthcare applications
Depending on your product’s target audience, you can achieve a number of operational and general improvements by implementing a blockchain. The good news is that most of these things can be achieved with the help of blockchain technology. Let’s take a look.
For healthcare providers
- Secure global data storage — Centralized storage of electronic medical records (EMRs) and patient records makes it’s easier for physicians from various medical institutions to access them. When stored in a global yet distributed system, these records are more structured and less fragmented than when they’re stored in proprietary systems. With global storage, data added to medical records is automatically synchronized between patients, medical facilities, laboratories, insurance companies, and other entities, saving time and sometimes lives.
- Strong access controls — Controlling access to patient data is one of the main goals of medical software. Access must be provided only to entities who need it and without fear that this information will be destroyed or tampered with. Ideally, access control can be carried out by the patient using a computer or mobile phone with biometric authentication. This will shift the focus in the healthcare system from medical facilities to patients.
- Efficient data transfer — Medical errors are the third leading cause of death in the United States. One common cause of medical errors is incorrect or missing data. If patient data were stored in one global system, these errors when transferring data between healthcare systems would simply disappear.
For first aid professionals
- Global database of medical records — Given access to a global database of medical records, an EMT would be able to find out a patient’s allergies and any ongoing treatments even if the patient were unconscious.
- Data synchronization — In the event of a global catastrophe, it’s crucial for rescue units from different countries to be able to quickly exchange critical data. In this case, a distributed global system could ensure smooth and secure synchronization during rescue missions, minimizing the risks of data falsification.
For patient monitoring
- Data from wearable devices — Today’s wearables collect valuable medical data every day, monitoring the quality of their users’ sleep and physical activity. It would be great if the readings of medical sensors and fitness trackers could be constantly and securely synchronized. In this way, a trusted doctor with access to this data would be able to monitor a patient’s health in near real time.
For doctors and patients
- Medical test data — Consolidating test results across facilities would increase reliability and eliminate the possibility of redundant lab testing. For example, doctors from areas without advanced equipment would be able to quickly get access to data from other laboratories instead of retesting a patient or asking them to share the results of previous medical tests. Additionally, consolidating such data in one place guarantees that medical workers will still have access to it even if the patient no longer has their own copy of the test results.
- Doctors’ profiles — Searching for the right doctor can be a challenge, so it would be great to have all the data needed for picking the right specialist in a centralized place. For example, a blockchain network could store the career history of healthcare professionals, allowing patients to easily search for the best specialists in a field.
- Data access management — Data access should be carefully controlled by both patients and doctors. For example, patients can allow doctors access to certain records and revoke access when it isn’t needed anymore. Or, when necessary, sensitive data like psychological assessments can be encrypted and hidden from patients.
For pharmaceutical companies
- Material and product tracking — The number of counterfeit medicines is only growing. The use of fake drugs leads to the deaths of 250,000 children per year. Pharmaceutical companies could fight this problem by deploying modern technologies like the blockchain to track the movements and storage conditions of medical products — or even raw materials for their manufacture. To make medicine distribution even more transparent, buyers should also be able to track the origins of purchased medical products and thus verify their quality.
For insurance companies
- Emergency data access — Insurance claims take a long time to process and involve many intermediaries. Insurance pre-authorization can’t be carried out reliably in cases when the patient is incapacitated (e.g. in the emergency room). This results in losses for healthcare providers due to rejected claims.
- Mitigating healthcare fraud — Sometimes patients try to get money from an insurance company by faking documents or providing inaccurate data. As a result, the annual cost of healthcare fraud has reached $68 billion in the US alone. A global consolidated data storage system would improve claim auditing and fraud detection.
- Insurance payment processing — To make the process as transparent as possible, payments between insurance companies, clients, and healthcare providers should be carried out via the same global network. This would lower the cost of remittances.
To tackle some of these issues, organizations develop an AI-based system for healthcare. In the next section, we discuss possible blockchain use cases in healthcare and take a look at the key pros and cons of enhancing medical software with blockchain features.
Pros and cons of using a blockchain in healthcare solutions
One of the defining characteristics of medical records is their high level of privacy. Data stored in healthcare applications is extremely sensitive, so it must be carefully protected from unauthorized access.
There are two key types of unauthorized access:
- Reading sensitive data without proper approval
- Tampering with private data
This is where you can effectively use a blockchain for healthcare. By design, a blockchain protects against data tampering. It makes it impossible to change data after it’s created. Changes can only be made incrementally, with even the smallest change recorded as a transaction in the blockchain ledger. And these records can’t be deleted or altered in any way. Originally, the immutability of stored data and the ledger structure of blockchains was designed to allow for the creation of digital currency like Bitcoin.
Immutability provides high trust in the data stored on the blockchain. Since that data can’t be changed or removed, it becomes a great source of common knowledge, especially with the addition of smart contracts.
When working with smart contracts, custom data can be stored and automatically handled by the blockchain. Today, smart contracts are widely used in fields such as transportation, logistics, finance, and IoT, ensuring both the transparency and security of valuable data. For instance, if used together with IoT technology, the blockchain can help pharmaceutical companies collect data from different sensors and track each movement of every product they have, from factory to shelf.
But when it comes to developing healthcare software, the blockchain offers a set of industry-specific advantages.
Key benefits of the blockchain in healthcare software
Blockchain technology in healthcare provides a unique opportunity for medical applications to add more value to the system. The biggest benefit a blockchain can provide in the long run is consolidating medical data into a single, reliable, and accessible source.
On a blockchain, data can be stored securely, with access managed by either patients themselves or their representatives. In this way, we can eliminate the risk of malicious or accidental disclosure of protected health information.
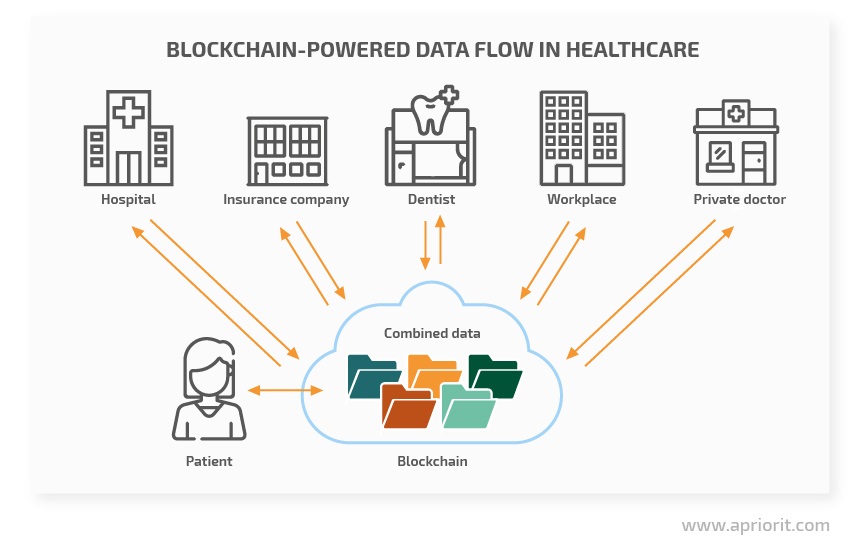
Such data aggregation would revolutionize the healthcare industry.
It’s true that blockchain technology is still evolving, but when implemented correctly, it comes with some hidden benefits. As the technology is new, it follows most industry best practices in terms of encryption, data protection, and access controls out of the box. In addition, blockchain integration makes you carefully consider the architecture of your software’s underlying systems, which can lead to the discovery of potential vulnerabilities that would likely have been missed in a solution developed with a conventional approach.
Additionally, security audits are a common practice in blockchain development. They involve experienced third-party auditors checking every aspect of a project for loopholes in the underlying logic to the configuration of the deployment and cloud security. Plus, blockchain-based systems are secure not only because of the inherent security of the technology itself but because of the careful design of most blockchain systems.
When healthcare and blockchain work together, it brings exciting innovations accompanied by important benefits:
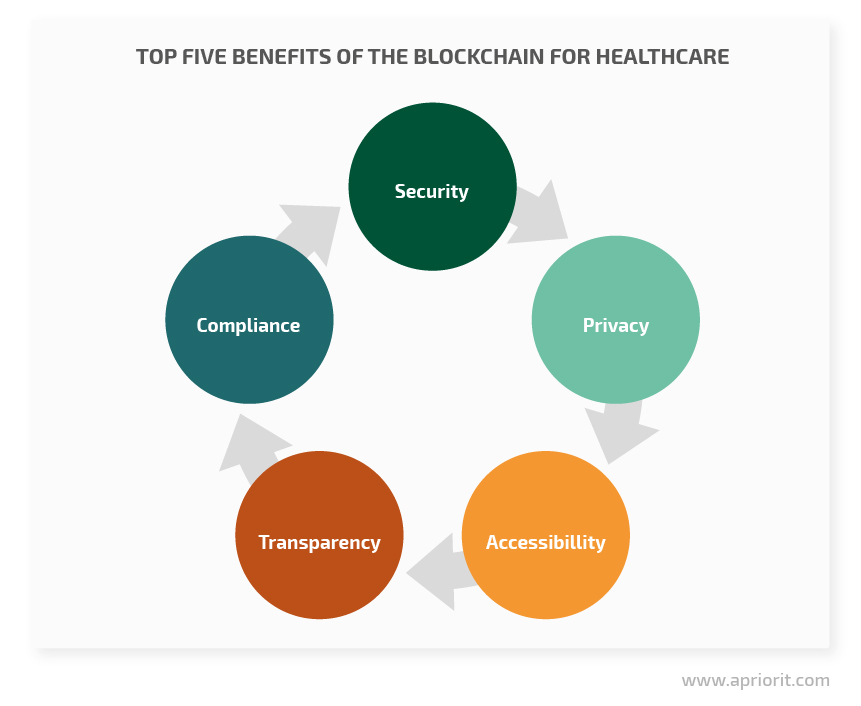
These benefits of the blockchain in healthcare are interconnected. Built-in data protection and immutability increase security and prevent data breaches. Enhanced security, in turn, makes it easier for healthcare applications to comply with government regulations. The strict rules of a blockchain network allow every participant to be confident in the data presented and to see the history of that data, making medical records transparent for all parties involved. Patients know what data is available and have full control of that data, making it readily accessible without multiple inquiries to several companies. And the ability to manage access to data and strong data security guarantee patient privacy.
However, as with any other promising solution, implementing blockchain technology comes at a price.
Read also:
Implementing Blockchain in Supply Chain: A Practical Example of a Custom Network Implementation
Pitfalls of blockchain adoption
One of the most common misconceptions about the blockchain is that it’s the ultimate solution to any problem. The unfortunate truth is that it’s not. For example, a blockchain can’t protect against human errors and social engineering attacks like phishing. Attackers can still hack individual devices and retrieve access keys from employees, so strict security policies and employee training are still a must for healthcare organizations.
Another downside of blockchain adoption is the difficulty of implementing a production-ready system. Designing an effective blockchain network requires a lot of time and skills. Depending on the task at hand, there’s little reason to create a brand-new blockchain network. Instead, it’s usually more effective to connect to an existing ecosystem. However, even when reusing resources, it’s not that easy to integrate a blockchain network with common technologies.
A lot of existing blockchain projects fail to pass the proof-of-concept stage and rarely deliver a quality minimum viable product (MVP). Launching and expanding a project with a blockchain is hard, and you’ll have to carefully consider your options and consult experts in order for your project to succeed.
The good news is that difficult doesn’t mean impossible. With thorough planning, you can build a reliable, secure, and effective blockchain-based healthcare solution. And to show how this challenge can be tackled, we’ve prepared an example application illustrating just how well a blockchain network fits into a data storage system.
Implementing a blockchain-based medical record management system
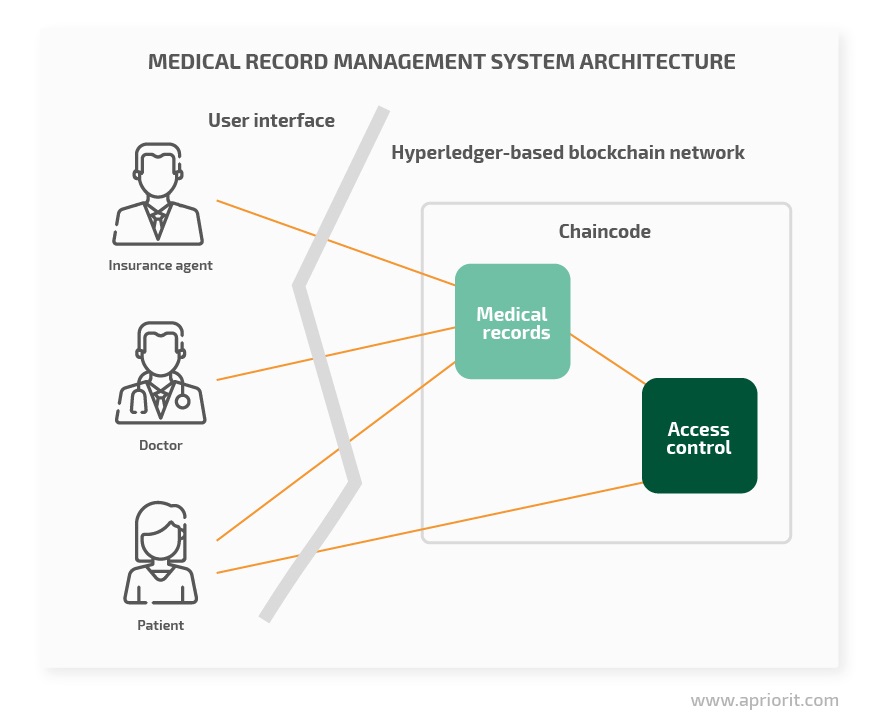
To better demonstrate how blockchain technology can help with improving storage and access to medical data, we’ve prepared a demo network based on Hyperledger Fabric. This network contains a smart contract for working with basic medical records.
To get a grasp of network configuration and smart contract development in Hyperledger, check out our previous post on building a Hyperledger-based network and enhancing it with custom business logic.
Now, let’s focus on how medical record management fits into the blockchain.
Disclaimer: The records presented in this example are not based on any real data from actual patients. However, they realistically represent the type of private data that may be stored in a similar production environment.
The data records in this demo are as simple as they get. The smart contract functions as a database of basic patient information and a history of medical visits. These records aren’t standard, however; thanks to the flexibility of smart contracts, they can easily be changed to store data from real-world databases.
By storing medical records on a blockchain network, we can present a single source of data to several organizations. In our demo, data is collected from three organizations. The key difference between creating a simple database and building a centralized blockchain-based database is the properties the blockchain brings: data immutability and traceability.
To ensure a secure and efficient exchange of information between patients, doctors, and nurses, we created a channel that provides a secure communication path between all actors in the system. No one outside this channel has access to its internal data.
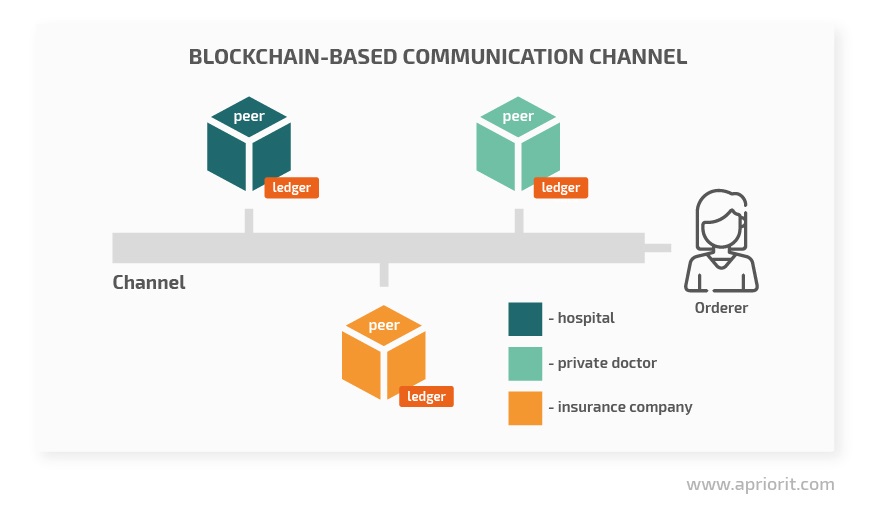
Different organizations that connect to the channel (e.g. hospitals, insurance companies, private doctors) have dedicated peers that are used for accessing the channel. One organization can have as many peers as it needs. Each peer hosts its own copy of the shared ledger, or rather the blockchain. Additionally, an orderer service is present in each channel in Hyperledger. The orderer maintains the channel and validates transactions. In our example, there is only one orderer, but more orderers can be added to scale the network.
A channel separates data from the external world and provides access control at the organizational level. However, it’s important to keep patient data hidden from other patients and unrelated personnel. Therefore, there must be a way to further protect patient privacy. In order to achieve such protection, two features of Hyperledger will be used:
- Encrypted private data collections. In Hyperledger, you can create a collection to ensure granular management of sensitive digital data. For example, you can join several organizations into a collection and use this collection to hide private data within a channel. Data within a collection isn’t shared with peers whose organization doesn’t belong to the collection.
- Permissioned data access via smart contracts. Permissioned data access allows us to further refine access based on custom policies. Our demo smart contract is pretty simple as it only provides read or write access. However, the smart contract could be improved to allow more fine-tuning and granular access control.
Our system was deployed locally for testing purposes using Docker containers. As there’s no graphical user interface (GUI) for Hyperledger, our developers needed to create a custom user interface. The most common option is to create a web-based interface, but you can also choose a desktop or mobile GUI. Such a GUI would call the Hyperledger API to execute actions in smart contracts. For simplicity, our demo uses a command-line interface (CLI) that’s provided with Hyperledger binaries.
Our demo has three types of users:
- Doctors can create and update patients’ medical histories.
- Patients can read their own medical histories and control who has access to their data.
- Insurance agents can only read a patient’s medical history data and only if the patient provides explicit permission.
Even in this simple example, the differences between a conventional database and a blockchain network become apparent:
| Blockchain | Database | |
| Physical data location | Decentralized across several peers | Centralized on a single server |
| Encryption | Built-in data encryption with additional access management | No built-in data encryption, possible encryption of the whole database |
| Access monitoring | Immutable history of every action | Access logs are stored separately and can be changed or deleted |
| Infrastructure | Expensive: Multiple medium to high-end nodes to act as peers and orderers | Cheap: Single medium-range server |
| Scalability | Built-in scalability of a distributed network | Requires custom replication solutions to achieve scalability |
| Implementation | Longer: complex architecture with multiple components | Faster: basic architecture that can be launched rapidly |
| Maintenance | Difficult: monitoring and maintenance of peer nodes | Easy: Single server with a single database |
| Development | Possibilities for improvements and integration with other systems by adding new smart contracts | Integration with other systems by cross-communication; fragmented data |
As you can see, a blockchain network can offer better protection for sensitive medical records than a traditional database. Thanks to built-in data encryption, decentralized storage, and immutable change history, a blockchain makes it nearly impossible to delete, alter, or tamper with sensitive data. Furthermore, by deploying additional blockchain features such as private data collections and premissioned data access, you can make sure that only authorized users get access to specific records.
At the same time, a blockchain-based network takes more time to build and requires extra resources and investments for its development and further maintenance compared to conventional databases. So the final choice will always depend on the specifics of the project at hand.
Conclusion
Opportunities for the blockchain in healthcare are exciting and nearly limitless. Currently, medical applications are one of the main targets of blockchain adoption as the benefits are simply too important to ignore.
By using the blockchain in the healthcare industry, we can ensure efficient defragmentation and consolidation of patient data. The blockchain also enables high-trust and high-transparency relationships between patients, medical service providers, insurance companies, and other healthcare entities. On top of that, a blockchain can provide additional access management capabilities and historical records of each instance of data access to improve the protection of personal information and prevent devastating data leaks.
There are countless possibilities to consider when implementing a blockchain network or when integrating a project with an existing blockchain. Choosing the right option and bringing your idea to life will surely require extensive knowledge and skills in the area of blockchain development. And this is where you could definitely use some help from blockchain experts.
At Apriorit, we have specialists passionate about creating blockchain solutions who understand the true importance of data security. Our team will provide the expertise necessary to lead your project to success. Get in touch with us and we’ll start discussing your project right away.



