Moving voting online can make the process more comfortable, more flexible, and accessible to more people. However, current electronic voting systems are also vulnerable to data compromise and voting result manipulations.
Knowing what your people think is vital. Gathering opinions and feedback from your community — citizens, employees, and customers — is at the core of the modern decision-making process. Yet relying solely on conventional voting mechanisms is becoming less convenient in both the public and private sectors. This is where solutions like a blockchain-based e-voting system come into play.
With global challenges such as the recent pandemic and the continually increasing speed of life, organizations should present tech-savvy users with an effective and secure alternative to paper-based ballots.
In this article, we talk about possible digital alternatives to traditional voting, the key benefits and challenges of using blockchain for voting, and what to pay attention to when building a blockchain-powered platform for online ballots.
Shifting towards digital polls and ballots
Paper-based offline voting is usually perceived as a secure, transparent, and reliable way to conduct elections and count votes. With paper ballots, you have a physical record of each vote and can audit and recount votes if necessary.
There are many cases when small and midsize businesses, large enterprises, and government and public organizations need to ask for the feedback from the community:

However, holding traditional paper-based votes on a regular basis is time-consuming and expensive. With national elections, for example, organizers need to account for voter registration systems, specific equipment for voting, high-quality paper for ballots, staff education, and media campaigns.
According to The Cost of Conducting Elections report [PDF] by MIT, the cost of conducting primaries and general elections in the US increased from $2.3 billion in 2016 to $5.7 billion in 2020. Some sources evaluate the overall cost of 2020 elections in the US as high as $14 billion, highlighting that this is more than twice as high as in 2016. And while part of the extra expenses in 2020 were associated with COVID-19 countermeasures, there’s an overall trend of rising election costs.
With employee surveys, the requirements for paper and equipment quality would be much lower than for national elections. Instead, we need to account for the costs of composing an appropriate questionnaire and analyzing survey results. While the final numbers depend on multiple factors, according to Driver Research, the average cost of a full-service employee satisfaction survey can range from $3,000 to $30,000.
Could there be a more affordable yet secure and effective alternative?
One possible solution to the problem of gathering and processing opinions on different topics quickly and with high quality is shifting to digital voting.
In Estonia, local elections are held via the e-Democracy service, which is part of a larger digital governing platform called e-Estonia. In Ukraine, the Diia service is used for public opinion surveys on such topics as Eurovision candidates and national postage stamp designs.
Today’s market offers two types of solutions for electronic voting:
1. Online polling platforms — Organizations often use ready products and services like Google Forms and SurveyMonkey when they need to gather feedback from stakeholders and customers. For employee surveys, it’s also common to use polling features in messaging apps: Microsoft Forms, Skype Poll, and Slack’s Simple Poll, to name a few.
These solutions are easy to use and work well for brief polls and gathering pointwise feedback. However, their security, data analysis, and customization capabilities are often limited.
2. Custom web applications — If organizations can’t find a fitting off-the-shelf product, they build custom solutions for polls and surveys. Depending on the particular case, it’s possible to create an advanced e-voting solution with a focus on the required set of features, be it extensive reporting customization or high-level data privacy protection.
We at Apriorit have vast experience building custom web platforms for unique industries and challenging tasks. In contrast to ready solutions, custom e-voting platforms enable organizations to choose the exact set of features and capabilities they need. As a result, they can build a secure electronic voting system without having to deploy multiple tools and pay for excessive functionality that will never be used.
The core reasons for organizations and businesses to use a digital surveying system include:
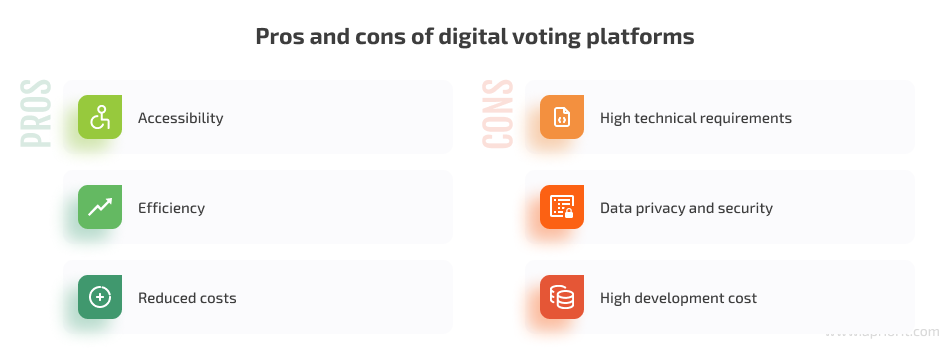
- Accessibility — Digital solutions can make it easier for people with limited physical abilities to participate in the voting process.
- Efficiency — E-voting platforms allow you to quickly create new polls, easily change them if needed, and process responses and deliver results in near real-time.
- Cost reduction — Digital voting services reduce the manual labor needed to hold a traditional ballot and are reusable and scalable, reducing costs in the long run.
However, shifting from paper-based ballots to electronic voting also has some downsides:
- High technical requirements — While electronic voting can eliminate physical access restrictions common for traditional voting, it can also be restrictive for people with no access to the necessary technology due to their location or financial means.
- Data privacy and security — With digital voting systems, protecting data privacy and ensuring the needed level of voter anonymity can be challenging.
- High development costs — Creating highly customized e-voting platforms that comply with necessary IT security standards requires rare skills and innovative technologies, which increases the overall development cost.
Digital platforms seem unlikely to fully replace traditional ballots just yet. However, we see governments and organizations worldwide making a significant shift towards a hybrid voting model combining these formats.
Looking for ways to enhance their solutions even more, creators of electronic voting solutions are leveraging various technologies, including the blockchain. In the next section, we discuss key reasons for organizations to consider adding a blockchain to the technology stack of their custom polling or surveying system.
Using a blockchain when building an e-voting solution
In an attempt to improve election processes, governments and the public in various countries have turned their attention to the blockchain. In Australia, there’s an initiative advocating the use of blockchain-based voting at the national level. And in the US, both the Republican and Democratic parties used the Voatz app during state conventions in several states.
The market also offers various blockchain solutions for online voting that businesses and organizations can leverage, such as Polys, Instars, and Real Research. Polys and Instars use the blockchain in a common way — to ensure secure yet transparent data storage, thus offering a secure digital voting system based on blockchain technology. Real Research takes a different approach and uses crypto as a reward for survey participants.
Organizations operating in both the public and private sectors can build a custom e-voting system using blockchain to conduct different types of surveys and votes:
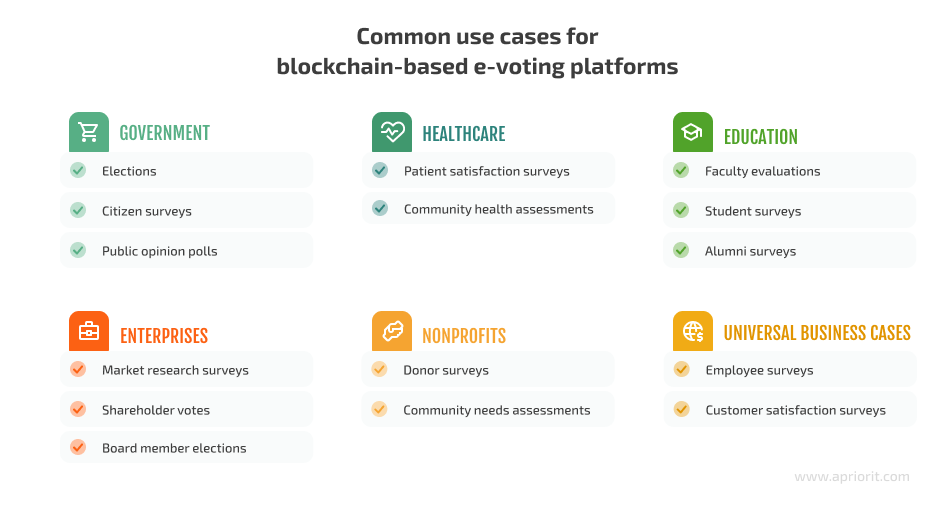
- Government — From citizen surveys to public opinion polls, governments can use a blockchain voting system as an alternative or companion to traditional voting methods.
- Healthcare — Healthcare organizations may conduct patient satisfaction surveys and assess community health needs.
- Education — Educational organizations can leverage blockchain technology in a voting system when conducting and processing regular student surveys, faculty evaluations, or alumni surveys.
- Enterprises — Businesses can use a blockchain-based e-voting system to conduct product and market research surveys, choose board members, and hold shareholder votes.
- Nonprofits — For nonprofit organizations, common use cases for solutions for digital voting with the use of blockchain technology include donor surveys and community needs assessments.
Aside from the listed use cases, organizations can use blockchain-based platforms for e-voting to gather feedback from their employees and stakeholders or conduct customer satisfaction surveys.
But what are the reasons for organizations to choose an e-voting solution that leverages blockchain technology?
We can outline four specific benefits of using blockchain for voting when building dedicated online solutions:
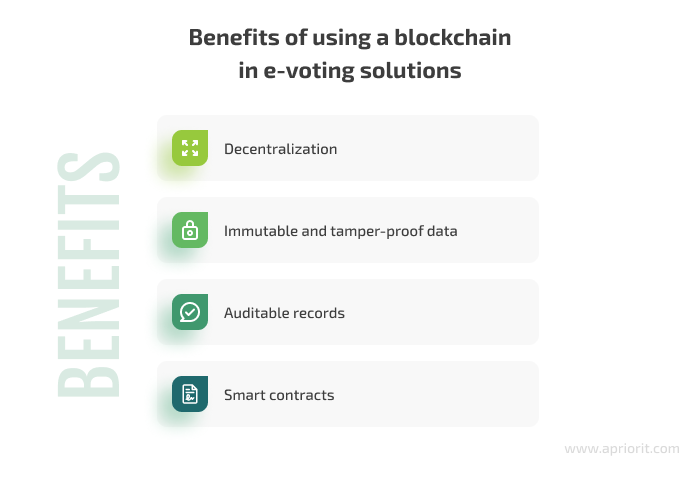
- Decentralization — Decentralized blockchains offer equality to all network participants, eliminating the risk of a certain centralized body overpowering all other users and forging vote results to their advantage. This ensures that the voting process is fair and unbiased.
- Immutable and tamper-proof data — Any change made to data stored on the blockchain is recorded automatically, making it impossible to stealthily manipulate or alter vote results.
- Auditable records — Being stored on the blockchain, voting results can be audited and verified by multiple parties.
- Smart contracts — Implementing smart contracts as part of an e-voting solution can help organizations automate critical processes, such as counting and verifying votes. With automated, transaction-like voting, organizations can also eliminate the risk of human error when counting votes.
However, incorporating the blockchain into an e-voting solution can be challenging for organizations and their development teams. In the next section, we cover the key technology-related limitations and pitfalls your developers may encounter when working on a blockchain voting system project.
Read also:
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Solutions: Benefits, Challenges, and Best Practices to Build One
Challenges and limitations of blockchain-based voting platforms
Despite the promising potential of enhancing e-voting solutions with the blockchain, there are certain challenges your development team should account for before starting this journey.
We can split these challenges into two categories:
Let’s first take a closer look at non-technical challenges.
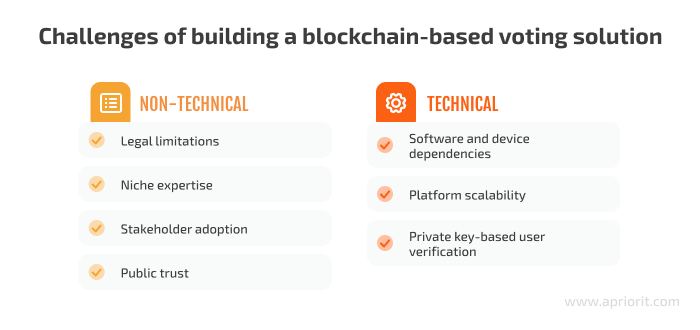
- Legal limitations — If your goal is to build a solution for government elections, both online voting and use of blockchains must be allowed in your region. If you build a solution for conducting polls and surveys of employees, stakeholders, and customers, you need to pay extra attention to relevant data privacy laws.
- Niche expertise — To build a secure and reliable blockchain-based online voting platform, your development team will need someone with extensive knowledge and experience in the field. Most organizations don’t have niche experts of this level on board, so it might be wise to consider outsourcing your blockchain development to a professional team like Apriorit.
- Stakeholder adoption — Alongside gathering a strong expert team, you’ll need to convince other stakeholders that the benefits of incorporating a blockchain into your online voting product outweigh the risks. At this stage, it would be nice to have a professional business analyst who can thoroughly evaluate the current state of the market. With deep analysis of market trends and competitor offerings, you can make the right technology and functionality choices and get strong arguments to win over your stakeholders.
- Public trust — To the general public, the blockchain is mostly known as the technological basis of the cryptocurrency world. Thus, your marketing team will need to work closely with end users to address their concerns and doubts when promoting the platform. Running an independent security audit of the platform and showcasing its results can help you increase the public’s trust in your product.
Aside from these challenges, there are specific technical limitations that your development team should account for when building an online blockchain-based voting system:
- Software and device dependencies — Like many digital solutions, a blockchain-based voting system is still dependent on the software and equipment used by voters. Hackers may use software or device flaws to steal a voter’s data or alter a vote before it’s recorded on the blockchain.
- Platform scalability — With blockchain-based platforms, sudden spikes of active users can lead to slower transaction processing and higher fees. Your team should account for this when choosing a blockchain network and architecture for your solution.
- Private key-based user verification — To verify a user’s identity, most blockchain platforms use unrestorable private keys. If a user loses access to their private key, they can be disqualified and thus unable to vote.
To overcome some of these challenges, you may consider limiting the use of blockchain technology in your online voting solution. Depending on the task at hand, the focus of your development team may range from ensuring the secure recording of votes on the blockchain to casting actual votes using smart contracts.
For example, you can use a blockchain only for storing vote results while leveraging other technologies for validating users and casting ballots. This is what researchers from Concordium Blockchain are currently looking into. Their goal is to evaluate if blockchain-based e-voting can increase voter participation, offering a secure solution to Greenland’s vote station accessibility issues.
No matter how extensively you want to use a blockchain in your e-voting product, there are several technical aspects your development team needs to pay special attention to. Let’s talk about them in the next section.
4 core aspects of building a blockchain-based voting solution
When using blockchain for an electronic voting system, your team will need to answer the following four questions:
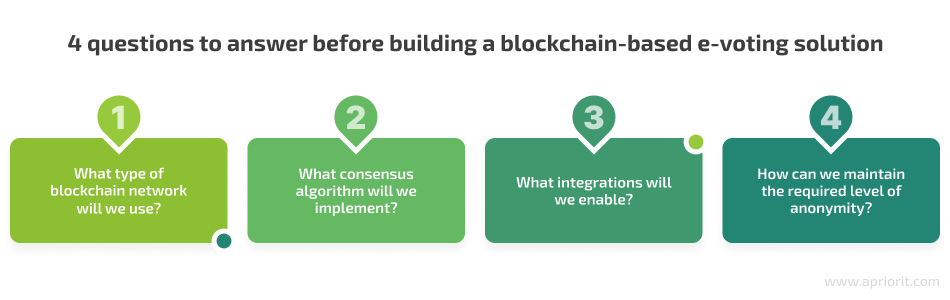
Let’s find answers to each of these questions.
1. What type of blockchain network will we use?
There are three common types of blockchain network architectures for your team to choose from:
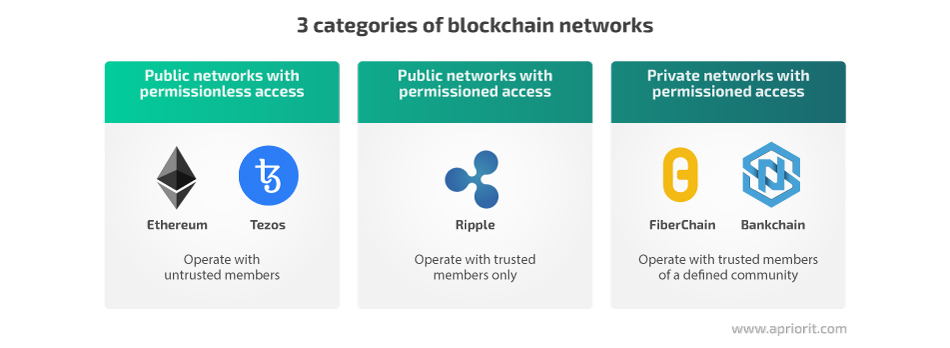
Your choice can be influenced by several aspects:
- Level of decentralization
- Information publicity
- Transaction fees
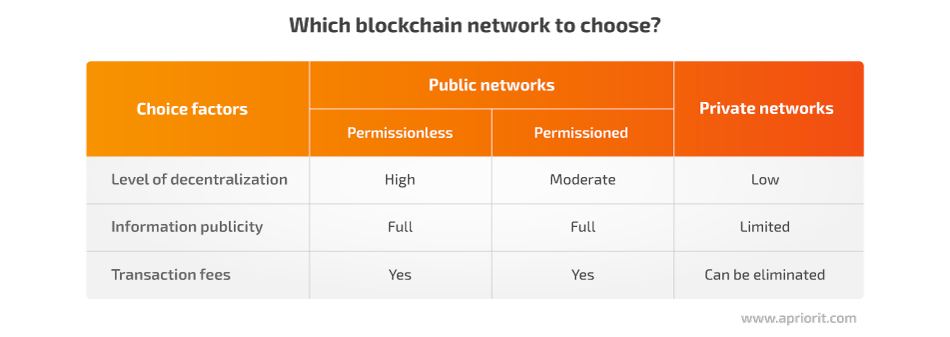
Permissioned networks are preferable for cases when only partial decentralization is desired. To achieve the maximum possible decentralization, a public permissionless blockchain would be best.
In public networks, all transaction information is available to everyone, so you can monitor election progress in real time. However, if you want to manage what data can be seen by the general public, you’d better go with a private blockchain network.
Finally, all public blockchain networks require a transaction fee (mostly as a security measure against denial of service attacks). While there are mechanisms that can make a transaction in a public network free for a user, it’s much easier to configure free transactions within a private blockchain network.
2. What consensus algorithm will we implement?
Consensus algorithms are responsible for reaching a single source of truth within a blockchain and can be competitive or non-competitive.
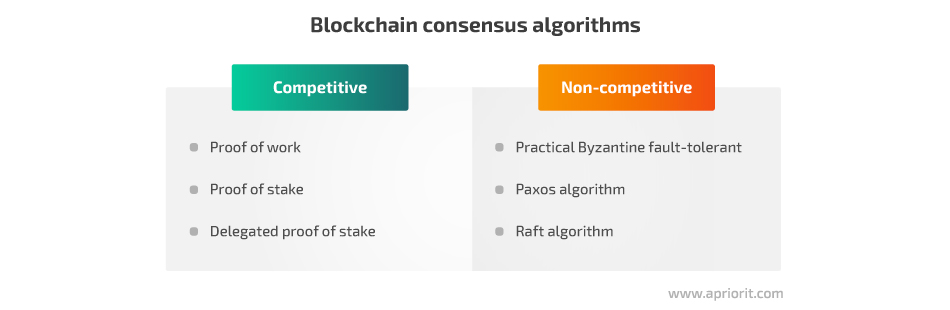
Competitive consensus algorithms were widely applied in the first blockchain models. While they can successfully achieve their main goal — reaching an agreement between nodes — they may be prone to double payment.
Non-competitive consensus algorithms, on the other hand, allow for processing only one agreement at a time in a trusted network. However, as networks relying on such algorithms usually consist of a small number of nodes, they can be more vulnerable to attacks than larger distributed ledgers with no single point of failure.
3. What integration opportunities will we enable?
While the blockchain has promising potential for use in the voting process, it won’t completely replace other voting approaches. Currently, digital voting solutions are most likely to be used in conjunction with traditional offline voting.
Your development team can leverage blockchain technology in a voting system to authenticate voters, cast ballots, and securely store identification and voting data. Thus, your blockchain-based solution might need to be able to integrate with:
- Third-party identity verification services
- Online voting systems
- Databases storing votes cast by other systems
Depending on the extent to which blockchain technology is used in your application, you need to plan different integration scenarios for each of these three options.
Also, when using a blockchain-based system alongside other electronic or offline voting approaches, it’s vital to make sure a user won’t be able to vote several times through different channels.
4. How can we maintain the required level of anonymity?
By default, blockchain transactions are public so that any user might access transaction details. However, online elections usually require ensuring complete ballot secrecy. So when building an e-voting system using a blockchain, it’s necessary to eliminate the possibility of linking a particular vote to a particular user. The only exceptions are cases where voter anonymity isn’t necessary, such as in parliamentary voting or when casting stakeholder ballots.
Many of the current blockchain-based voting systems rely on non-interactive zero-knowledge arguments as a measure for achieving the right balance between ballot secrecy and verifiable voting results.
After answering these four questions, your development team will be able to outline the basic set of requirements for your blockchain-based e-voting solution.
Conclusion
Building a custom digital voting platform can help organizations make data-driven decisions and reduce administrative overhead and human errors. With a blockchain, you can enhance such platforms with features such as automated transactions, traceable operations, and immutable data records. In contrast to regular online voting platforms, blockchain-based solutions also provide a high level of voting transparency and protect against fabricated vote results.
Apriorit’s blockchain development experts can assist your organization with designing and delivering a custom web solution enhanced with blockchain-based capabilities.
Reach out to start discussing the details of leveraging blockchain technology for your business!


