In one of our previous articles, we considered the basics of Windows driver testing. Our experts explained the Windows device driver testing process.
In this article, we dig deeper into Microsoft’s testing process, called Windows Hardware Quality Labs (WHQL) testing. We explain the deployment of WHQL infrastructure and the WHQL testing flow. This article will be useful for quality assurance specialists who are preparing Windows drivers for Microsoft Hardware Certification.
What is WHQL testing?
Windows Hardware Quality Labs is a testing procedure that allows you to test the reliability and compatibility of your device or driver with Windows operating systems. Successfully passing all the tests makes it possible to get Microsoft Hardware Certification for your device or driver. Moreover, this opens the door to get your driver distributed through Windows Update or the Microsoft Update Catalog.
During the WHQL testing procedure, you run a series of tests to verify the quality of your driver on third-party hardware or software. Then you submit the log files for Microsoft to review. In case of a successful Windows driver certification via WHQL tests, Microsoft will send you a WHQL release signature file that you should add to the driver installation package. This Windows Hardware Certification confirms that your driver is compatible with Windows.
Previously, Microsoft charged a fee for WHQL certification, but now the procedure is free.
WHQL testing is performed with a special toolkit depending on the target operating system. There are three of them:
- Windows Hardware Lab Kit (Windows HLK)
- Windows Hardware Certification Kit (Windows HCK)
- Windows Logo Kit (Windows LK)
Table 1 below shows which version of which kit should be used with a given operating system.
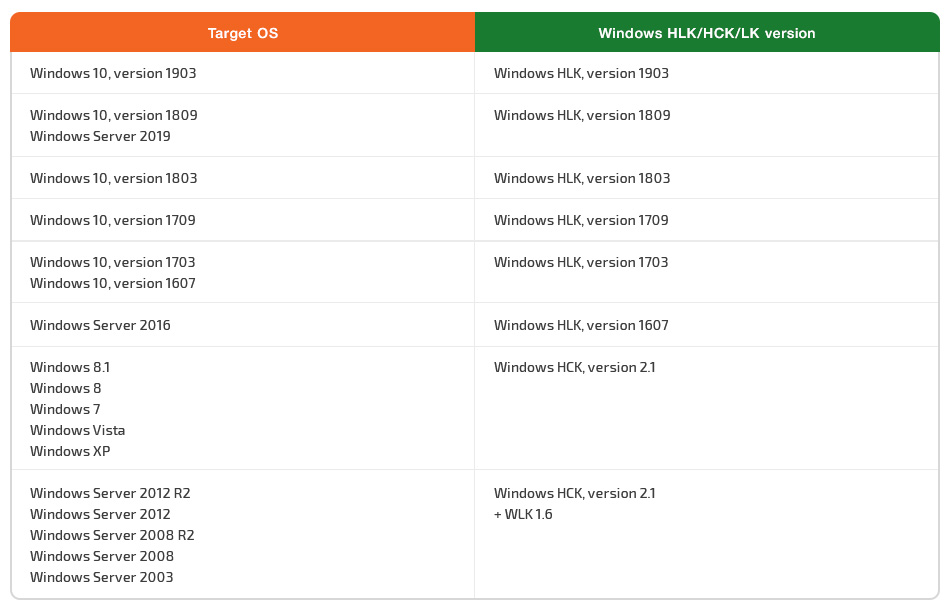
Table 1. WHQL toolkit versions according to the target operating system
Ready to start a new driver project or improve an existing one?
Rely on Apriorit’s expert driver developers to receive the solution that meets all your needs and requirements.
Why do you need Microsoft Hardware Certification?
Without Microsoft Hardware Certification, a user will see a warning message when installing your driver. This message says that Windows can’t verify the publisher of the software or that your software has not passed Windows Logo testing to verify its compatibility with Windows.
If you obtain a WHQL release signature, you’ll get a “Certified for Windows” logo (or something similar) to use on your product packaging and advertising as well as a WHQL release signature verifying the source and legitimacy of your driver.
WHQL certified drivers are included in the Microsoft Compatibility Center, which provides the latest updates to the Windows operating system. This allows end users to download your driver automatically when they use a device for the first time.
With WHQL driver certification provided by Microsoft, your driver gets better test coverage. This allows testers to find almost all driver defects and let developers fix them before the driver release. The WHQL testing process also helps test centers better support the driver device. Microsoft driver certification proves that a driver has been tested thoroughly with Microsoft-approved QA standards.
In addition, Microsoft Hardware Certification prevents driver tampering. This is great from a security perspective, but it also means that any driver updates will require your driver to pass WHQL testing again.
Let’s take a closer look at the process of WHQL testing and obtaining Microsoft Hardware Certification.
WHQL infrastructure deployment
WHQL testing requires a specific test environment. Table 2 shows what components should be prepared to perform testing with Windows HLK for Windows 10 clients.
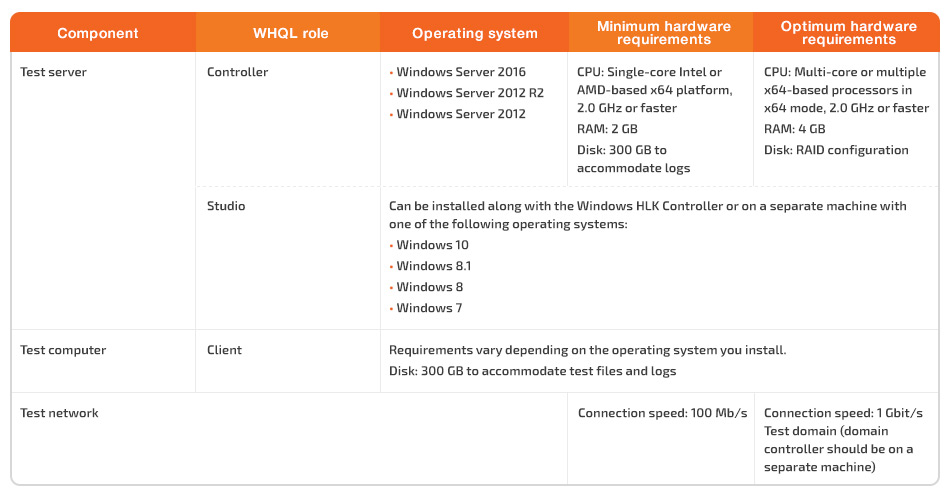
Table 2. WHQL infrastructure components using the example of Windows HLK for Windows 10 clients
Installing the Windows HLK Controller and Studio doesn’t take much effort. You just need to download and run the setup file of the kit corresponding to the target operating system. During installation, you need to allow a port to be opened. Otherwise, the installation may fail. Installing the HLK Controller and Studio took us approximately 45 minutes.
The Windows HLK Client takes just several minutes to install on the test computer using an installer file. If the test computer is not a member of the local network domain, the Guest account should be enabled on it. To begin the installation, it’s first necessary to mount the test server’s shared folder – called HLKInstall – with its subfolder named Client, as shown in Image 1.
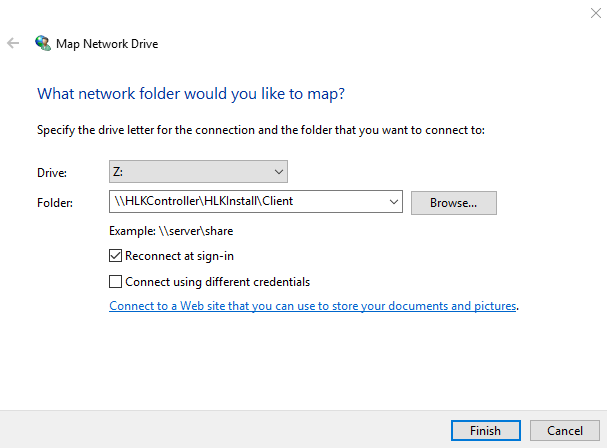
Image 1. Mounting the Windows HLK Controller’s shared folder on the test computer
From the mounted folder, it’s enough to run the Windows Command Setup.cmd (see Image 2). It will determine the computer’s processor architecture and launch the appropriate installer.
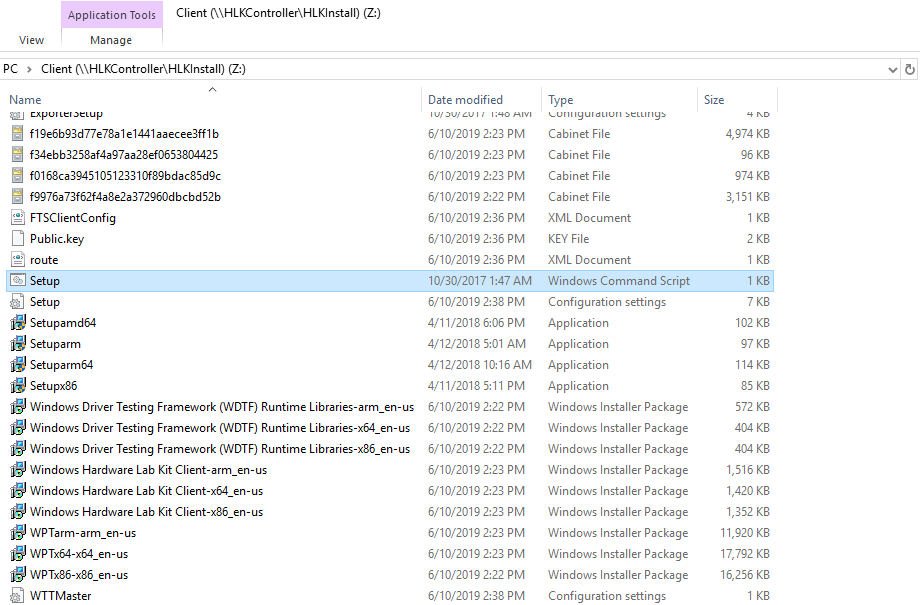
Image 2. Run Setup.cmd to start installing the Windows HLK Client
Read also
How to Develop a Windows Driver Using a QEMU Virtual Device
Uncover Apriorit’s approach to developing Windows drivers with the help of a QEMU virtual device. Explore all the benefits and limitations of device emulation for driver development and receive a clear overview on how to establish communication between a device and its driver.
WHQL testing flow
The testing process with WHQL can be divided into five steps:
- Create a machine pool
- Create a test project
- Select a target
- Select and run tests
- Analyze the results
Let’s take a closer look at each of these steps.
To perform testing, you’ll probably have to operate with a certain group of test computers. Such a group in Windows HLK is called a machine pool. It defines on which machines you want to test.
By default, all new clients are placed into the default pool. However, this pool can’t be used for testing purposes. So you have to create a new one. To do this, launch HLK Studio on the test server and click the Configuration button at the top of the page. Then, select $ (Root) and choose the Create Machine Pool option in the context menu. You can rename your pool as you want (see Image 3).
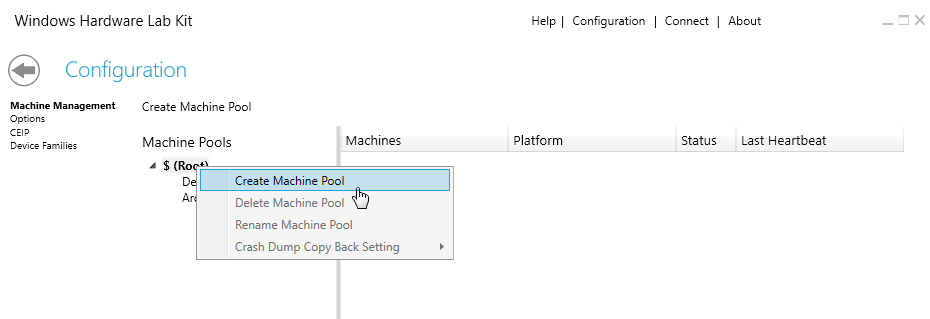
Image 3. Creating a machine pool
After the pool has been created, just drag and drop your client from the default pool into the new pool as shown in Image 4.
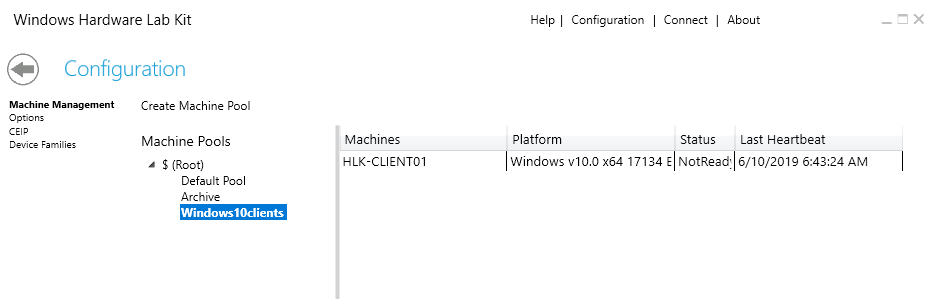
Image 4. Drag and drop the client into the custom machine pool
Switch the client to the Ready status in the context menu. This makes the client initialize on the test computer and get ready for testing. If you forget to switch the status, you won’t be able to proceed with testing the client.
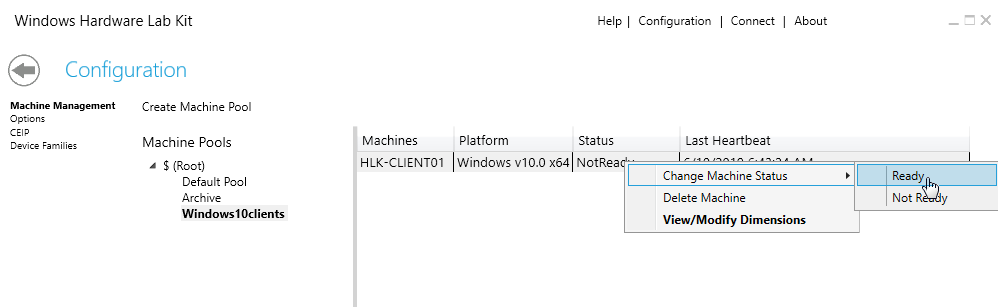
Image 5. Switch the client into Ready status
The next step is to create a project, which defines what you want to test. To create one, you just need to click the Create project button in Windows HLK Studio.
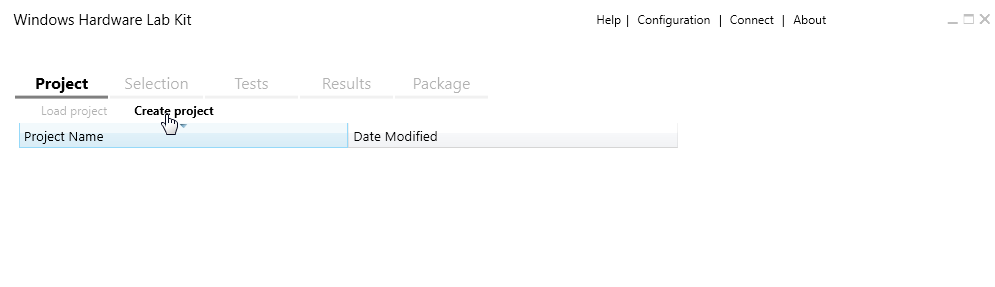
Image 6. Create a new project
Here, you can also enter a custom name for the project. If the project wasn’t loaded by default (in which case its name should appear under the Project tab), you can provide a custom name via the context menu.
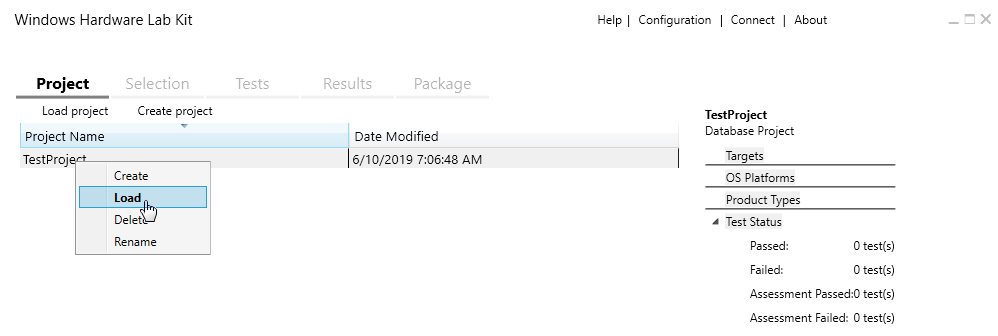
Image 7. Load the created test project via the context menu
The next step is to select a target to be tested. A target in Windows HLK is an individually testable feature that your device or driver implements. To select one, click on the Selection tab under the name of your project and choose your pool of clients.
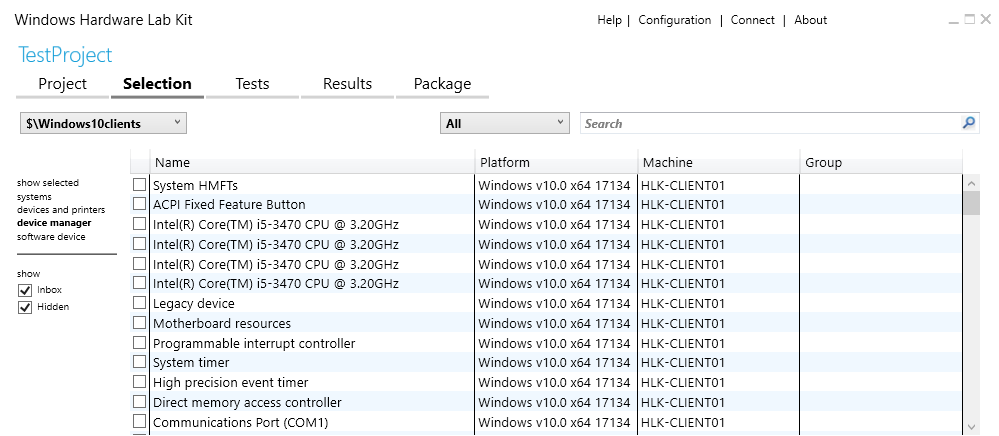
Image 8. Selecting a target for testing
As you can see from Image 8, targets can be filtered by the following options:
- show selected – displays only the selected targets
- systems – used to test a complete client
- device and printers – used to test an external device connected to a test system
- device manager (selected by default; has the most detailed view) – used to test a component of a test system
- software device – used to test filter drivers, firewalls, and antivirus software installed on the test system
It’s necessary to select all the features of a specific product type for a device or driver to receive Microsoft Hardware Certification.
The Tests tab in Windows HLK Studio shows the tests for the selected target. All tests are categorized by the test phase as shown in Image 9.
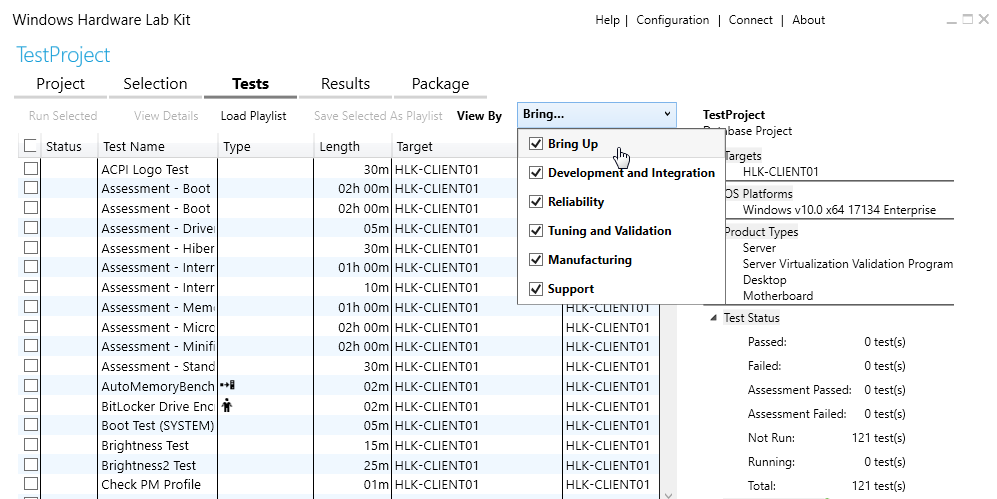
Image 9. Test categorization by test phase
Let’s look closer at each category of tests:
- Bring Up tests verify that the device works properly at launch. Examples of Bring Up tests include disabling and enabling devices with I/O before and after, sleep with I/O before and after, etc.
- Development and Integration tests include all tests needed to check the correct device implementation and integration with the system. Examples include removing the device, compliance tests, and the HyperVisor Code Integrity Readiness test.
- Reliability tests verify that the device will work in extreme conditions, such as when faced with thousands of create-open-close sequences or I/O operations during reboot and restart. Examples of reliability tests are fuzz open and close tests and reboot-restart with I/O during disk stress.
- Tuning and Validation tests include signature verification, INF file verification, and TDI filter verifications.
- Manufacturing tests can include such verifications as Secure Boot logo test, signed driver check, and battery validation.
- Support tests, such as the ApiValidator test, verify whether the device will be easy to maintain.
It doesn’t matter that different test phases might include the same test. For instance, the Sleep with I/O before and after test is suggested by HLK Studio in two phases – Development and Integration and Reliability. The difference is in the way the test is conducted. At the Development and Integration phase, the test lasts only about 5 minutes, whereas at the Reliability phase it’s run much longer – about 45 minutes. A detailed description of each test can be found on the HLK Test Reference page.
To select a specific test in HLK Studio, just check the box and click on Run Selected (Image 10).
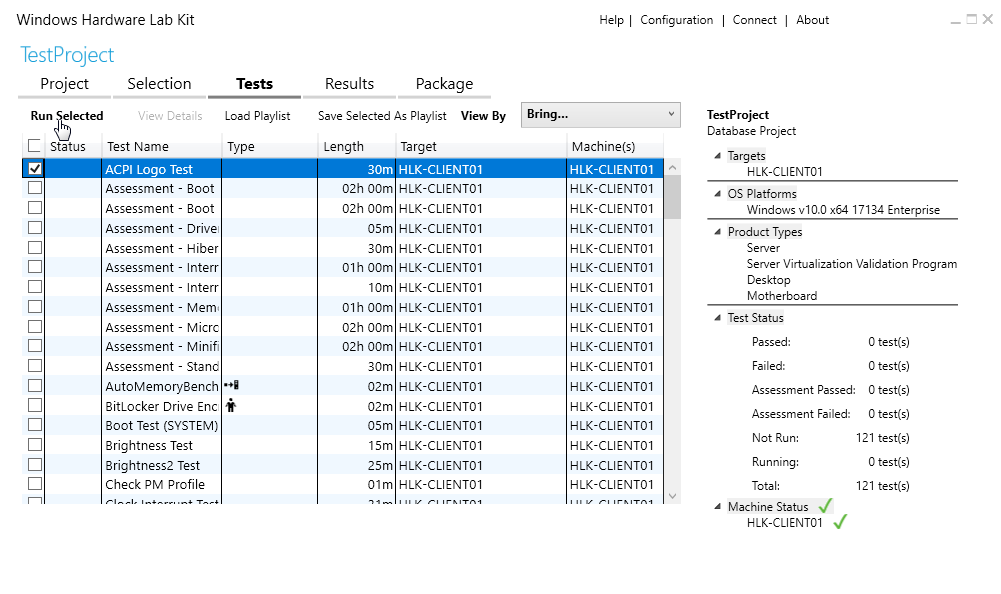
Image 10. Select and run a test
The results of the tests are displayed in the Results tab. After each test is completed, the status column is updated with the result: pass or fail.
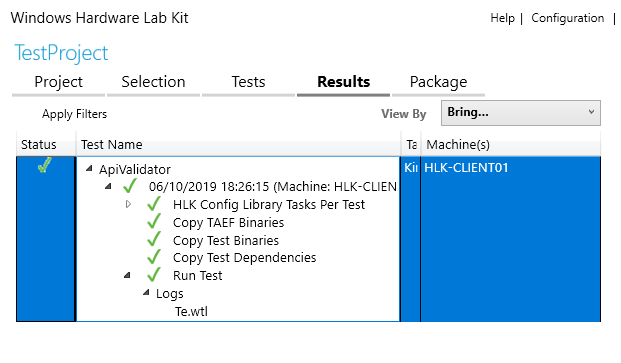
Image 11. Example of the ApiValidator test result
To see the details of any test, you can use log files. A log file has the .wtl extension and can be opened with the Windows HLK Manager included in the kit.
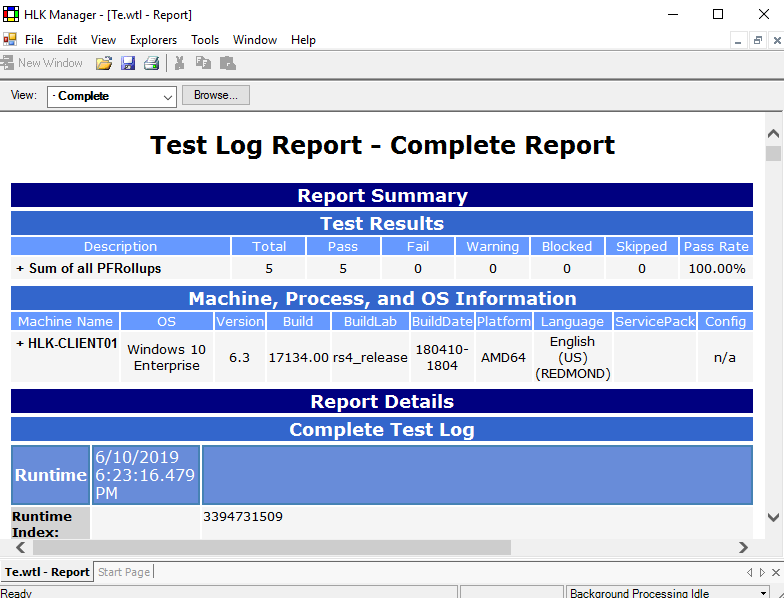
Image 12. Test log report in the Windows HLK Manager
If any test has failed, you can find a description of the error in the report.
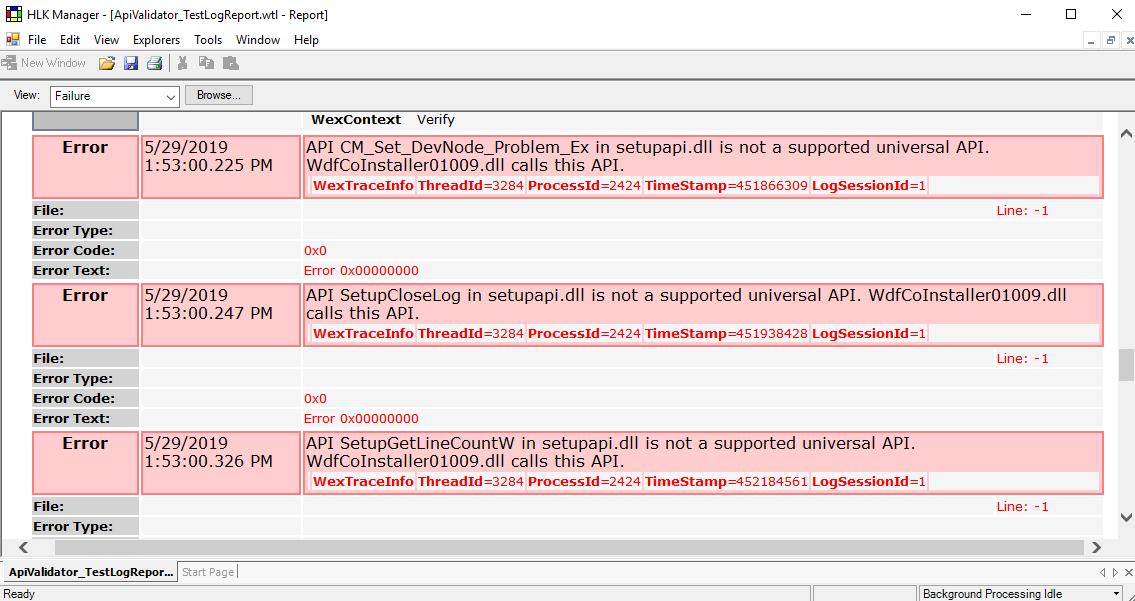
Image 13. Failed test log report in the Windows HLK Manager
After the reason for the test failure is eliminated, the test can be run again.
Related project
Improving a Windows Audio Driver to Obtain a WHQL Release Signature
Discover the details of improving the audio driver for the Windows version of client’s AI-powered sound filtering application. Find out how Apriorit developers helped our client successfully obtain a WHQL certification.
Getting Microsoft Hardware Certification
If all tests for the selected target have been passed successfully, there will be an option on the Package tab of the Windows HLK Studio to create a package that can be sent for certification by Microsoft (see Image 14).
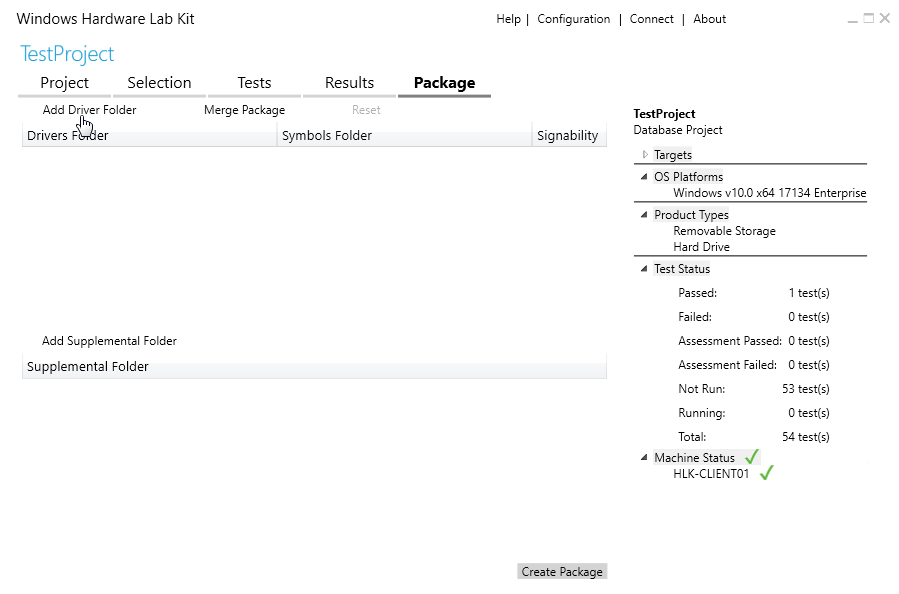
Image 14. The Package tab in Windows HLK Studio
You can add the driver, symbols (via the context menu of the added driver), and a supplemental folder (Readme files, error descriptions, etc.) to the package if needed.
Click the Create Package button to generate the package. Here, the following signing options will be suggested:
- Do not sign
- Use the certificate store
- Use a certificate file
The form for submitting the package for signing by Microsoft is available here (authorization with a Microsoft account is required).
Conclusion
In this article, we described the Windows Hardware Quality Labs testing infrastructure deployment and Windows driver certification process using the example of the Windows Hardware Lab Kit for Windows 10.
Here are some tips for testers who are going to check their drivers with Microsoft WHQL certification and testing:
- Use a dedicated test environment with a high-speed connection
- Schedule your tests carefully, as their execution could take a lot of time (you can see the approximate time in the Tests tab opposite each test)
- Take into account that some tests will require user interaction, so prepare for them in advance
- Refer to the WHQL troubleshooting articles if any issues occurs
The Apriorit team uses the Windows Hardware Lab Kit not only to get Microsoft Hardware Certification for drivers we develop but also to ensure driver quality for our clients. We have dedicated teams with expertise in driver development and quality assurance services ready to assist you with projects of any complexity.
Need help with driver development and testing?
Get yourself an exact driver your business needs and receive assistance with preparing the product for any certification you have in mind. Delegate solving all the tricky issues to Apriorit developers!




